Difference between revisions of "Test Tasks"
m |
m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
"An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports on a craft's velocity, orientation, and gravitational forces, using a combination of accelerometers and gyroscopes, sometimes also magnetometers..." © [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inertial_measurement_unit Wikipedia] | "An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports on a craft's velocity, orientation, and gravitational forces, using a combination of accelerometers and gyroscopes, sometimes also magnetometers..." © [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inertial_measurement_unit Wikipedia] | ||
| − | We use [http://www.analog.com/en/mems-sensors/mems-inertial-measurement-units/adis16375/products/product.html ADIS16375] (fully compatible with [http://www.analog.com/en/mems-sensors/mems-inertial-measurement-units/adis16488/products/product.html ADIS16488]) | + | We use [http://www.analog.com/en/mems-sensors/mems-inertial-measurement-units/adis16375/products/product.html ADIS16375] (fully compatible with [http://www.analog.com/en/mems-sensors/mems-inertial-measurement-units/adis16488/products/product.html ADIS16488]) with a tri-axis gyroscope and a tri-axis accelerometer. |
{| | {| | ||
|valign='top'|[[File:NC353L-369-IMU-GPS 4 comments.jpeg|300px|thumb|IMU, [http://www.analog.com/en/mems-sensors/mems-inertial-measurement-units/adis16375/products/product.html ADIS16375] in NC353L-369 camera]] | |valign='top'|[[File:NC353L-369-IMU-GPS 4 comments.jpeg|300px|thumb|IMU, [http://www.analog.com/en/mems-sensors/mems-inertial-measurement-units/adis16375/products/product.html ADIS16375] in NC353L-369 camera]] | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Our projects=== | ===Our projects=== | ||
| − | ====Relative | + | ====1. Images Relative Orientation==== |
| − | The goal is to find the camera's | + | The goal is to find how the camera rotated/moved ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotation_matrix Rotation Matrix]) between the shots. Knowing the images' relative orientation allows to use this information for further 3D reconstruction. |
| + | |||
| + | ====2. ERS Correction==== | ||
| + | Our sensor is Aptina's [http://www.aptina.com/products/image_sensors/mt9p006i12stc/ MT9P006] - CMOS, 5MP, 1/2.5". It has an ERS ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rolling_shutter Electronic Rolling Shutter]) - the image scan time is about 1/15 s (~66 ms) while IMU samples data at 2.460 kHz (T = 0.406 ms) which makes it possible to reconstruct how the camera moved during the image acquisition and correct the ERS effect by placing each pixel according to the sensor orientation at each moment of time. This only corrects the movement/rotation of the camera but not the ERS from the moving objects. | ||
===Test Task 1: Parsing Data=== | ===Test Task 1: Parsing Data=== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 20: | ||
===Test Task 3: Finding the camera orientation === | ===Test Task 3: Finding the camera orientation === | ||
===Test Task 4: Reconstructing camera rotation during the sensor scan=== | ===Test Task 4: Reconstructing camera rotation during the sensor scan=== | ||
| + | ===Links=== | ||
| + | * [[10338|10338 Sensor board]] | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 13 September 2012
Contents
Area: IMU Data Processing
About
"An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports on a craft's velocity, orientation, and gravitational forces, using a combination of accelerometers and gyroscopes, sometimes also magnetometers..." © Wikipedia
We use ADIS16375 (fully compatible with ADIS16488) with a tri-axis gyroscope and a tri-axis accelerometer.
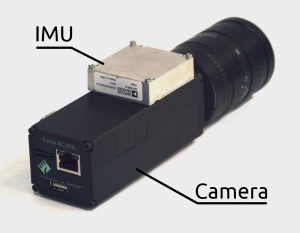 IMU, ADIS16375 in NC353L-369 camera |
Our projects
1. Images Relative Orientation
The goal is to find how the camera rotated/moved (Rotation Matrix) between the shots. Knowing the images' relative orientation allows to use this information for further 3D reconstruction.
2. ERS Correction
Our sensor is Aptina's MT9P006 - CMOS, 5MP, 1/2.5". It has an ERS (Electronic Rolling Shutter) - the image scan time is about 1/15 s (~66 ms) while IMU samples data at 2.460 kHz (T = 0.406 ms) which makes it possible to reconstruct how the camera moved during the image acquisition and correct the ERS effect by placing each pixel according to the sensor orientation at each moment of time. This only corrects the movement/rotation of the camera but not the ERS from the moving objects.
