Difference between revisions of "Kifu: Go game record (kifu) generator"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| − | 2. The selection is rectified using a perspective correction matrix | + | 2. The selection is rectified using a perspective correction matrix. |
[[Image:kifu_rectify.jpg]] | [[Image:kifu_rectify.jpg]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| − | 5. Finally, after filtering intersections and interpolating missing ones | + | 5. Finally, after filtering intersections, looking at the number of intersection for each aligned row or column, and interpolating missing ones (or better); we can validate the region or restart at step 1 with another threshold |
Revision as of 14:20, 23 August 2008
Goban and Grid Detection:
1. The input image is filtered and thresholded and a big quadrilateral shape is selected, sorting contours detected with OpenCV.
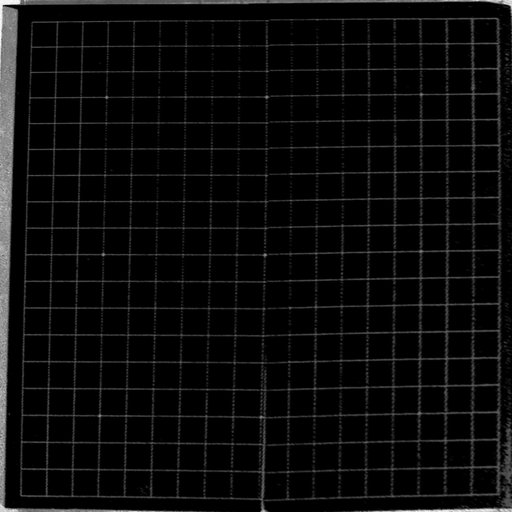
2. The selection is rectified using a perspective correction matrix.
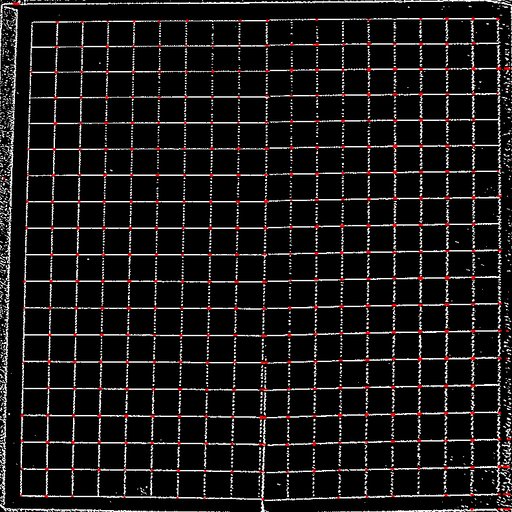
3. OpenCV find lines in the rectified selection and we compute the intersections for each detected line segment.
4. After, we round the results to group close neighbour points, and compute or approximate the center of each group (ie: intersection)
5. Finally, after filtering intersections, looking at the number of intersection for each aligned row or column, and interpolating missing ones (or better); we can validate the region or restart at step 1 with another threshold
Image change detection:
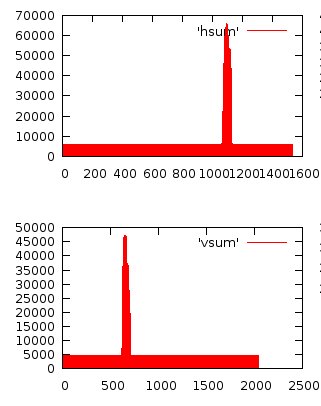
Using vertical and horizontal RGB components sums of a thresholded difference between a reference image and the current one,
it is easy to compute the image coordinates of a played stone
Stone detection:
When a stone is played it overlaps 1 grid square on a corner, 2 on the borders and 4 in the center.
Computing horizontal and vertical pixel sums for each grid cell or around each intersection can tell where the stone is played and reveal the color of the stone, being darker or brighter than the empty intersection region.
The intersection can also be seen on the difference image when the stone is white, that could also be used to detect the stone color.
Methods for mapping the coordinates:
"2.2 Perspective transformation with two vanishing points"
(pages 2 and 3, equations 7 and 10)
http://cipa.icomos.org/fileadmin/papers/potsdam/2001-21-gf01a.pdf
Inverse homography and plane image rectification (page 14)
http://www-prima.imag.fr/jlc/Courses/2002/DEA-IVR.VO/DEA-IVR.VO.S2.pdf
"Inferring Projective Mappings" (page 3)
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.9.7803
with related java and C source code here: http://www.developpez.net/forums/showthread.php?t=591698
Links:
http://www.sourceforge.net/projects/kifu
http://opencvlibrary.sourceforge.net/
Photointerpretation and Small Scale Stereoplotting with Digitally Rectified Photographs with Geometrical constraints:
http://cipa.icomos.org/fileadmin/papers/potsdam/2001-21-gf01a.pdf
Vision par Ordinateur:
http://www-prima.imag.fr/jlc/Courses/2002/DEA-IVR.VO/DEA-IVR.VO.S2.pdf
Projective Mappings for Image Warping:
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.9.7803
http://sciences.ch/htmlfr/geometrie/geometrieprojective01.php