Difference between revisions of "Eyesis4Pi 393"
From ElphelWiki
(→Calibration) |
(→Calibration) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
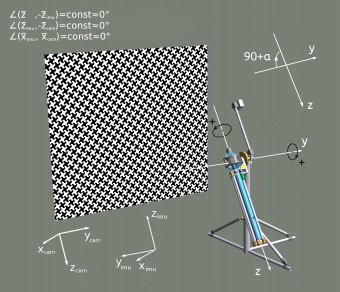
The [[Eyesis4Pi_Calibration|calibration]] is performed using the machine ('''goniometer''') that rotates the camera about 2 axes (y & z on the drawing) by precisely known angles. To calibrate IMU one needs to match the goniometer angles with the IMU data. | The [[Eyesis4Pi_Calibration|calibration]] is performed using the machine ('''goniometer''') that rotates the camera about 2 axes (y & z on the drawing) by precisely known angles. To calibrate IMU one needs to match the goniometer angles with the IMU data. | ||
| − | Check out | + | Check out these articles for more details: |
| + | * [http://blog.elphel.com/2012/09/building-and-calibrating-eyesis4%CF%80/ Building and calibrating Eyesis4Pi] | ||
| + | * [http://blog.elphel.com/2013/06/elphel-new-camera-calibration-facility/ New calibration facility] | ||
| + | |||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 10:02, 22 December 2016
Contents
Status
Available
Overview
Elphel Eyesis4Pi-26-393 is the newer generation of the full-sphere multi-camera systems for stereophotogrammetric applications.
Automated panoramic imagery and 3-dimensional panoramas are the 2 main applications of Eyesise4Pi-393 camera. * Car and backpack mounts are not included. Improvements over older generation Eyesis4Pi
|
Features
- 4*π (360x180) full sphere coverage
- 64 MPix panoramic image resolution after stitching
- Final panoramic image equirectangular projection dimensions - 14000x7000
- 0.05 Pix stitching precision
- Calibrated fixed lens to compensate for the lenses distortions
- 10" (0.1 pix) in the center 80% x 80% area
- 30" (0.3 pix) maximal error over the full FoV
- <0.03um/° thermal expansion
- 5 FPS - maximum frame rate
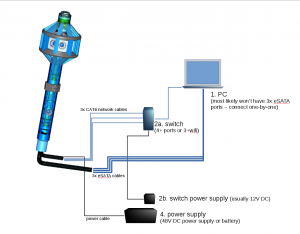
- Integrated high-precision IMU and GPS
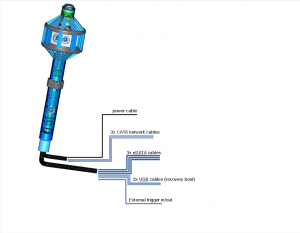
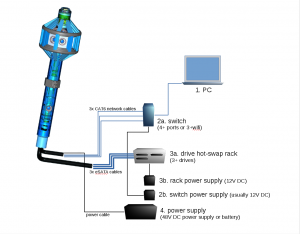
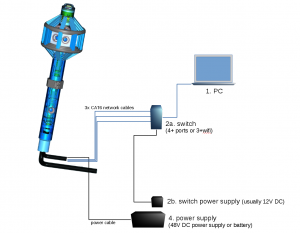
- Recording to:
- internal SSDs
- external SSDs
- a PC over network
- Web Based GUI
- Free Software and Open Hardware
Calibration
We have developed full calibration process and post-processing software to compensate for:
- Optical aberrations, allowing to preserve full sensor resolution over the camera FoV.
- Distortions – for precise pixel-mapping for photogrammetry and 3D reconstruction.
The calibration is performed using the machine (goniometer) that rotates the camera about 2 axes (y & z on the drawing) by precisely known angles. To calibrate IMU one needs to match the goniometer angles with the IMU data.
Check out these articles for more details:
3D Model
|