Elphel Eyesis4Pi
Contents
[hide]- 1 Brochure Download
- 2 About
- 3 Tech specs
- 4 More Information
- 5 FAQ
- 5.1 Why are there 8 SSDs and not just a single bigger one?
- 5.2 Can I also use Eyesis4Pi with HDDs instead of SSDs?
- 5.3 How do I unload the data from Eyesis4Pi?
- 5.4 What software do I need on my laptop/computer to control Eyesis?
- 5.5 How do I connect my laptop/computer to Eyesis and how do I control image recording?
Brochure Download
Eyesis 4Pi Brochure Download V24
About
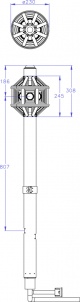
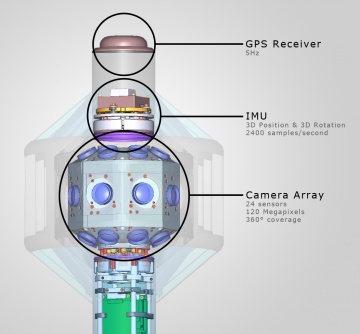
Elphel Eyesis4Pi is an open hardware / free software panoramic camera solution that is able to capture high-resolution - 64 MPix total (120 MPix before stitching) - 360° panoramas at a rate up to 5 frames per second at full resolution. It is the successor of the Elphel Eyesis. Images are recorded to 8 solid-state-discs (Eyesis4Pi Data Storage) which can store up to 11 hours of footage at full resolution. Meta-data like GPS-coordinates (geotags), viewing direction, movement speed, etc. are directly embedded into the images EXIF fields. Eyesis4Pi uses 24 sensor-front-ends and high-grade lenses that are triggered simultaneously with microsecond accuracy to ensure a full homogeneous spherical snapshot.
Usage Scenarios
The system was designed to be small and lightweight with a minimal distance between the entrance pupils (46.5mm) to achieve lowest possible parallax.
The primary usage scenario is to mount Eyesis4Pi on the roof of a vehicle. When driving at 50 mph (22.3 m/s) and recording at 5 FPS a full panorama is captured every 4.46 meters.
Operation & Monitoring
Eyesis is controlled from a laptop, via a web-based interface (Eyesis GUI). Which also displays real-time previews of your captured panorama footage.
Eyesis is supplied with 110V/220V AC and can be used with car power adapter (inverter), when mounted on a car roof. Power consumption is around ???W.
Models
4π (or 4Pi) corresponds to a full full spherical (360°x180°) field of view in steradians.
There are 2 version of the camera Eyesis4Pi with 24 image sensors and full spherical field of view and Eyesis3Pi with 16 sensors (without 8 bottom modules) with slightly smaller field of view.
Comparison between Eyesis and Eyesis4Pi
| Parameter |
Eyesis |
Eyesis4Pi (Eyesis 3Pi without 8 bottom modules) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combined field of view (steradians) |
3*π |
4*π (3*π) | |
| Number of image sensors |
9 |
24 (16) |
|
| Angular resolution +/-30° from the horizon |
≥4.2Mpix/steradian |
≥4.2Mpix/steradian |
1 |
| Angular resolution +30° to +90°(zenith) |
≥0.83Mpix/steradian |
≥4.2Mpix/steradian | 1 |
| Angular resolution -30° to -90°(nadir) | none | ≥4.2Mpix/steradian (none) | 1 |
| Combined megapixels | 45.0 | 120.0 (80.0) | |
| Combined megapixels (w/o overlapping areas) | 34.0 | 64.0 (48.0) | |
| Combined megapixels (w/o overlapping areas, worst case resolution) |
29.0 | 52.8 (39.6) | 1,2 |
| Distance between entrance pupils of adjacent horizontal lenses |
34.5mm | 46.5mm | |
| Distance between entrance pupils of horizontal and top/bottom lenses |
75mm | 50mm | 3 |
| Maximal frame rate | 5fps | 5fps | 4 |
| Maximal recording data rate | 48MB/s | 128MB/s (96Mb/s) | |
| Maximal direct network data rate | 30MB/s | 80MB/s (60MB/s) | |
| GPS receiver | external, USB | External/internal, USB/RS232 | |
| GPS pulse-per-second input | no |
yes |
|
| IMU | none | ADIS163xx,ADIS164xx | |
| Data unload | removable SSD in cradles | eSATAx2 | |
| Storage devices type | 2.5″ SSD | 1.8″SSD | |
| Number of storage devices | 3 |
8 (6) |
|
Notes:
- Angular resolution per pixel differs in the sub-camera FOV, minimal resolution is used.
- Zenith area for Eyesis (covered by fisheye lens) is calculated separately.
- For Eyesis the distance is measured from the entrance pupil of the horizontal lens to that of the top fisheye, for Eysis-4pi – to the entrance pupil of the lens immediately above/below the first one.
- Frame rate may be limited by the recording (or network if the SSD are not used) datarate for high compression quality (>0.3 bytes/pixel), required for the aberration correction.
Calibration
The sensor-front-ends (SFE) - which were especially developed for Eyesis4Pi - allow the focus plane to be shifted and rotated with very high accuracy. This allows extremely precise calibration of each lens and SFE which is done with every Eyesis4Pi during assembly with custom developed software. Check out this Elphel Development Blog post for more details.
Tech specs
Eyesis4Pi Camera
- 24x Color 5MPix CMOS sensors in array that covers the sphere
- 2x Color 5MPix CMOS sensors in the pole that make stereo pairs with corresponding sensors in the camera head.
- Resolution - 64MPix (120MPix before stitching)
- Up to 5 FPS at full resolution (120Mpix) - only if equipped with SSDs
- Web-based GUI
- GPS powered geo-tagging
- IMU powered 3D inertial measurement
- Precise image capture synchronization
- RAW or compressed image formats
- High resolution lenses: 24x M12 lens mount
- Very small parallax - distance between entrance pupils: 46.5 mm
- Weatherproof camera body and camera pole
- Highly Customizable
Eyesis Data Storage
- located inside weatherproof camera pole
- 8x swappable ???GB - 1.8" - SSDs (Total ???GB)
- Enough space for up to ?? hours of full Resolution/FPS footage (depending on quality settings and actual image content)
Eyesis Computer
The Eyesis Computer is a high-end-workstation with small form factor. It is intended for image post-processing and not required for recording footage.
It comes with all Elphel developed software and tools required for processing panoramic images preinstalled.
- Small form factor Shuttle PC
- Intel Core i7-950 Quad-Core Processor
- 16 GB DDR3 RAM
- GeForce GTX 465 (Fermi) 1GB
- 2 TB HDD
Tech Specs of a Single Image Sensor (Eyesis4Pi uses 24 of these, Eyesis3Pi uses 16 of these)
| Color Image Sensor | 1/2.5" bayer-pattern CMOS |
| Effective number of pixels | 2592x1936 (5,018,112 pixels) |
| Aspect Ratio | Chip 4:3, Region of interest freely adjustable in 16 pixel steps |
| Sensor Output | 12 Bit ADC |
| Sensor Features | Region of interest, on-chip binning and decimation |
| Dynamic Range | 70 db (76 db at 2x2 binning) |
| Electronic Shutter | 1 us to "very long" (~3h) in 1us steps |
| Gain | Analog & Digital (0 db to 12 db continuous) |
==
More Information
Wiki:
Elphel Development Blog:
- Current state of the Eyesis project Introdcution of Eyesis4Pi
- “Zoom in. Now… enhance.” – a practical implementation of the aberration measurement and correction in a digital camera
- “Zoom in. Now… enhance.” – Results
- Elphel Eyesis camera optics and lens focus adjustment
- Elphel-Eyesis, assembled
- Elphel-Eyesis Progress
- First Elphel Eyesis Prototype assembled
FAQ
Why are there 8 SSDs and not just a single bigger one?
There are 24 sensor-front-ends. There are 8 system boards each connected to 3 sensor-front-ends and one SSD. So the shots of a single panorama are split up on 8 SSDs. 3 images to SSD1, 3 images to SSD2, 3 images to SSD3, etc.
Can I also use Eyesis4Pi with HDDs instead of SSDs?
We initially tested the system with HDDs but due to strong vibrations when using Eyesis mounted to a car roof we experience massive write-rate drops with HDDs. After we switched to SSDs all these problems were gone. If your Eyesis application does not involve bumby roads or vibrations HDDs should work just fine though.
How do I unload the data from Eyesis4Pi?
The camera pole has 2 eSATA ports in a weatherproof sealed connector. With this connector you can connect to the SSDs inside the camera pole like to any external hard-drive with any laptop/computer.
What software do I need on my laptop/computer to control Eyesis?
Eyesis GUI requires a locally running webserver (apache2 + PHP5) and the Eyesis User Guide software.
How do I connect my laptop/computer to Eyesis and how do I control image recording?
The Eyesis4Pi hosts a Gigabit Ethernet switch so all you need is one Ethernet cable from the camera pole hose to your laptop/computer.
The Eyesis GUI is completely browser based so after you connected to the network you just start a browser type in the correct URL and you are ready to go.